Table of Contents
Ask Us Any Question
1. Introduction: Why Fire Resistance Is a Structural Requirement, Not an Option
In modern construction, fire safety is not a supplementary feature—it is a fundamental requirement. Buildings today must meet stringent fire regulations to protect occupants, property, and investment. Among the many solutions, fire rated boards play a critical role as a passive fire protection measure, providing a tested and certified barrier against the spread of flames and smoke.
While many refer colloquially to “fireproof boards,” the professional terminology distinguishes between fire rated board and fire resistant board. A fire rated board is a material that has undergone standardized testing to ensure it can withstand fire for a defined period, whereas fire resistant boards may offer partial protection but may not meet formal certification standards. The term “fire board” is often used broadly to describe any board with some fire-resistant properties, which can include gypsum, fiber cement, mineral wool, or magnesium oxide (MgO) boards. Understanding these distinctions is essential for architects, engineers, and contractors specifying materials for commercial, residential, or industrial projects.
By integrating fire rated boards into walls, ceilings, partitions, and enclosures, designers create safe compartments within buildings. These boards do not simply resist flames—they preserve structural integrity, limit heat transfer, and reduce smoke emission. In critical areas such as high-rise buildings, hospitals, data centers, and industrial facilities, the right fire rated board can save lives and mitigate property damage.
2. What Is a Fire Rated Board?
A fire rated board is a construction material certified to resist fire for a specified duration, commonly ranging from 30 minutes to 120 minutes. Unlike general fire boards, which may slow the spread of flames without formal verification, fire rated boards have undergone controlled laboratory testing under recognized international standards such as EN 13501, ASTM E119, or BS 476. These tests evaluate the board’s ability to maintain structural integrity, limit heat transfer, and minimize smoke and flaming droplet emission during a fire event.
2.1 Fire Rated vs. Fire Resistant vs. Fireproof
-
Fire Rated Board: Certified through standardized testing, with defined performance under fire conditions. Required for compliance in many building codes.
-
Fire Resistant Board: Offers some fire protection, but may not be formally tested or certified. Suitable for low-risk or supplementary applications.
-
Fireproof Board: A common marketing term, rarely technically accurate. No board is entirely “fireproof,” but proper fire rated boards provide predictable resistance.
-
Fire Board: Broad category including all boards with some level of flame resistance, regardless of certification.
Understanding these terms helps project teams make informed decisions, ensuring the selected material aligns with legal requirements and performance expectations. Not all fire boards are suitable for critical applications—only boards that pass rigorous testing provide reliable protection.
2.2 Key Features of Fire Rated Boards
-
Structural Integrity: Ability to retain shape and support loads during exposure to fire.
-
Heat Insulation: Limits temperature rise on the unexposed side, protecting occupants and sensitive building components.
-
Smoke and Droplet Control: Reduces smoke density and prevents flaming debris from spreading, a key factor in evacuation safety.
-
Certifications: Official labels and test reports verify compliance with standards, providing confidence for engineers, contractors, and building inspectors.
Fire rated boards are available in various compositions—gypsum, fiber cement, mineral wool, calcium silicate, and magnesium oxide (MgO)—each offering distinct properties such as moisture resistance, durability, and structural support. Selecting the right board requires considering fire rating duration, building code requirements, and the specific environmental conditions of the project.

3. International Fire Rating Standards
Fire rated boards are not all created equal. Their performance and classification are governed by internationally recognized standards, which provide architects, engineers, and contractors with consistent, reliable metrics for safety and compliance. Understanding these standards is essential for selecting the right board for each building type and geographic region.
3.1 EN 13501 (Europe)
The EN 13501 series is the primary European standard for classifying building materials according to fire performance. Boards tested under this standard receive ratings for combustibility, fire resistance, smoke emission, and flaming droplets. For example:
-
A1: Non-combustible, no contribution to fire
-
A2-s1, d0: Essentially non-combustible, minimal smoke, no flaming droplets
These classifications guide designers and contractors in choosing materials that meet both local building codes and European fire regulations, ensuring safe evacuation and protection of structural components.
3.2 ASTM E119 (United States)
In the United States, ASTM E119 defines the fire resistance of building assemblies, including walls, ceilings, and floor systems. Testing evaluates:
-
Structural Integrity: Can the board sustain load under high temperatures?
-
Heat Transfer: How well does it prevent the spread of heat to unexposed areas?
-
Flame Spread & Smoke: Measures the ability to limit fire progression and smoke hazards
Fire rated boards certified under ASTM E119 are often rated in hour increments (1-hour, 2-hour, 4-hour), directly informing their application in commercial, residential, and industrial projects.
3.3 BS 476 (United Kingdom)
One of the oldest fire standards, BS 476, assesses materials based on integrity, insulation, and load-bearing capacity. Boards tested under BS 476 provide critical information for approvals in high-risk environments, such as hospitals, schools, and public transportation hubs.
3.4 Other Regional Standards
Depending on the region, boards may also need to comply with:
-
ISO 834 (international fire resistance test for structural elements)
-
GB 8624 (China, classification of combustibility of building materials)
Compliance with recognized standards ensures that the board performs as expected in fire conditions and meets legal requirements for construction safety.
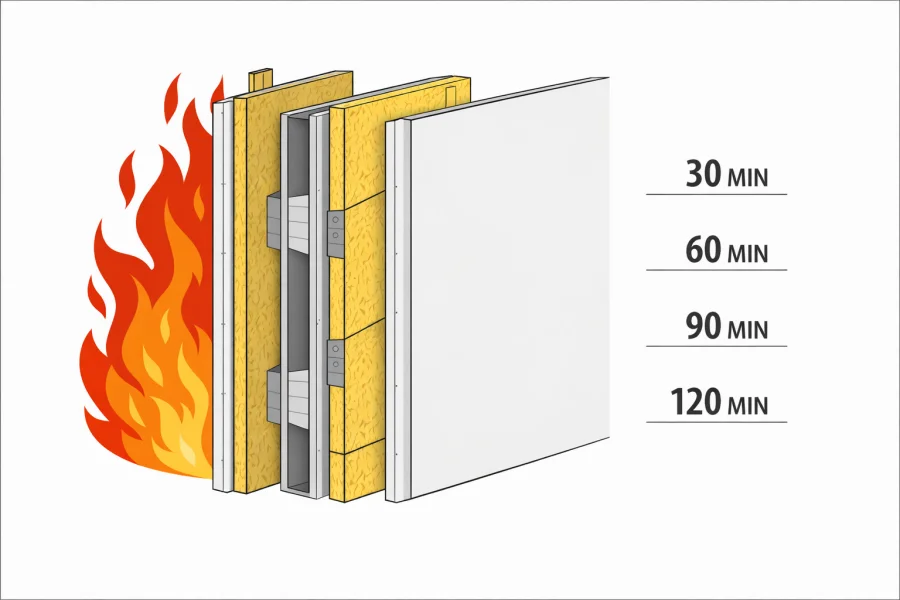
4. Fire Resistance Ratings: 30, 60, 90 & 120 Minutes
Fire rated boards are categorized by the duration they can withstand fire while maintaining structural integrity and limiting heat transfer. Selecting the correct rating is crucial for occupant safety, code compliance, and project cost-effectiveness.
4.1 30-Minute Fire Rated Board
-
Maintains integrity for 30 minutes under fire conditions
-
Commonly used in low-rise buildings or interior partitions with minimal fire exposure risk
-
Suitable for non-load-bearing applications
4.2 60-Minute Fire Rated Board
-
Provides 1-hour fire resistance
-
Widely used in residential, commercial, and educational projects
-
Allows sufficient time for evacuation and fire service intervention
4.3 90-Minute Fire Rated Board
-
Recommended for areas with higher safety requirements, such as stairwells, corridors, or commercial ceilings
-
Ensures compartmentalization and fire containment in multi-story buildings
4.4 120-Minute Fire Rated Board
-
Offers 2 hours of fire resistance
-
Ideal for high-risk zones, including hospitals, laboratories, industrial facilities, and high-rise constructions
-
Critical for areas with heavy occupancy or sensitive operations
4.5 Key Considerations for Selecting Ratings
-
Building Type and Occupancy: High-rise or public facilities often require higher ratings
-
Risk Assessment: Areas with flammable materials or critical operations may need extended protection
-
Cost-Benefit Balance: Over-specifying can increase cost without significant safety gain
Understanding the rating ensures that fire rated boards, whether gypsum, fiber cement, calcium silicate, mineral wool, or MgO boards, are applied correctly, maximizing fire safety, compliance, and long-term performance.
5. Major Types of Fire Rated Boards: Technical Comparison
Choosing the right fire rated board requires understanding the material types, performance characteristics, and suitability for specific applications. Not all fire boards are created equal, and different boards excel under different conditions. Here is a technical overview of the most commonly used boards in modern construction:
5.1 Gypsum Fire Board (Fire-Resistant Drywall)
-
Composition: Gypsum core, often with additives for enhanced fire resistance
-
Fire Resistance: Typically 30–60 minutes depending on thickness and reinforcement
-
Applications: Interior partitions, ceilings, low to mid-rise residential and commercial buildings
-
Advantages: Lightweight, easy to cut and install, widely available
-
Limitations: Vulnerable to moisture; not suitable for high-humidity areas without protective coatings
5.2 Calcium Silicate Board
-
Composition: Silica and lime mixture, reinforced with fibers
-
Fire Resistance: 60–120 minutes; can withstand higher temperatures than gypsum
-
Applications: Industrial facilities, kitchens, laboratories, stairwells, high-temperature environments
-
Advantages: High thermal stability, load-bearing capability, moisture-resistant
-
Limitations: Heavier than gypsum, requires skilled installation
5.3 Fiber Cement Board
-
Composition: Cement, sand, cellulose fibers
-
Fire Resistance: 60–120 minutes depending on thickness
-
Applications: Exterior cladding, ceilings, industrial interiors
-
Advantages: Excellent moisture and weather resistance, durable, long lifespan
-
Limitations: Heavier; cutting generates dust; installation may require power tools
5.4 Mineral Wool Board
-
Composition: Rock or slag fibers, bound with adhesive
-
Fire Resistance: 90–120 minutes; non-combustible
-
Applications: High-rise buildings, mechanical rooms, acoustic partitions
-
Advantages: Superior thermal insulation, sound absorption, high fire resistance
-
Limitations: Brittle; requires protective facings; heavier handling
5.5 Magnesium Oxide Board (MgO Board)
-
Composition: Magnesium oxide, magnesium chloride, reinforcing fibers
-
Fire Resistance: 60–120 minutes; non-combustible
-
Applications: Hospitals, schools, residential and commercial high-rise buildings, industrial facilities
-
Advantages:
-
Moisture and mold resistant
-
Lightweight yet strong
-
Durable and long-lasting
-
Environmentally friendly (low VOC)
-
Compatible with steel structures
-
-
Limitations: Slightly higher upfront cost than gypsum or fiber cement boards
-
Why It Stands Out: MgO boards combine fire performance, moisture resistance, and structural strength, making them an ideal choice for high-performance construction projects
5.6 Technical Comparison Table
| Board Type | Fire Rating | Moisture Resistance | Load-Bearing | Installation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gypsum | 30–60 min | Low | Low | Easy |
| Calcium Silicate | 60–120 min | Medium-High | High | Skilled |
| Fiber Cement | 60–120 min | High | Medium | Moderate |
| Mineral Wool | 90–120 min | Medium | Low | Moderate |
| MgO Board | 60–120 min | High | High | Moderate |
This comparison highlights that no single board type is universally superior; selection depends on fire rating requirements, environmental exposure, load-bearing needs, and installation logistics. However, for projects where high fire performance, moisture resistance, and long-term durability are all critical, magnesium oxide boards provide a balanced solution unmatched by most alternatives.
6. Seven Critical Facts Most Buyers Don’t Know About Fire Rated Boards
Even experienced architects and contractors sometimes underestimate the nuances of fire rated boards. Understanding these seven facts can prevent costly mistakes, ensure compliance, and maximize safety:
6.1 Fire Rating Applies to the Entire Assembly, Not Just the Board
A common misconception is that the fire resistance of a wall or ceiling depends solely on the board. In reality, the rating includes the board, supporting structure, joint treatments, fasteners, and coatings. Using uncertified boards or improper installation can void the rating, leaving buildings at risk despite using high-quality materials.
6.2 Moisture Significantly Affects Fire Performance
Boards exposed to high humidity or water can lose structural integrity, reducing fire resistance. Magnesium oxide and fiber cement boards are naturally moisture-resistant, while gypsum boards often require additional protection in wet areas to maintain their fire rating.
6.3 Not All “Non-Combustible” Materials Are Equal
Labels like A1 or A2-s1,d0 indicate non-combustibility, but they don’t guarantee load-bearing capacity, impact resistance, or long-term durability. Choosing the right board requires evaluating mechanical and environmental performance, not just fire classification.
6.4 Weight Impacts Installation and Performance
Heavier boards, such as calcium silicate or mineral wool, require stronger supporting structures and specialized fasteners. Overlooking weight considerations can complicate installation, slow construction, and increase labor costs.
6.5 Installation Quality Directly Affects Fire Resistance
Even the highest-rated board will underperform if installed incorrectly. Gaps, improper fastening, or unsealed joints can reduce fire containment, allowing smoke and flames to spread. Certified boards should always be installed according to manufacturer instructions and tested assembly guidelines.
6.6 Certification Authenticity Matters
Counterfeit or misleading certifications are a real concern in international supply chains. Always verify batch numbers, test reports, and compliance logos. Recognized standards include EN 13501, ASTM E119, BS 476, and ISO 834.
6.7 Over-Specifying Fire Ratings Can Increase Costs Without Benefits
Using a 120-minute board where a 60-minute rating suffices raises material and labor costs unnecessarily. Conducting a project-specific risk assessment ensures safety while optimizing budget and resources.
6.8 Why These Facts Matter
Understanding these insights helps project teams:
-
Select the appropriate board type for each project zone
-
Avoid installation errors that compromise fire safety
-
Make cost-effective decisions without sacrificing compliance
-
Identify high-performance boards, like MgO boards, that combine fire resistance, moisture durability, and structural support
By integrating these critical facts into design and procurement processes, building owners and contractors can ensure that fire rated boards perform as intended, protecting lives, assets, and regulatory compliance.

7. Key Applications in Modern Construction
Fire rated boards are essential in modern construction, not just for regulatory compliance, but for occupant safety, property protection, and long-term building performance. Their use varies by building type, fire risk, and functional requirements. Understanding these applications ensures the right board is specified for the right location.
7.1 High-Rise Buildings
High-rise structures present unique fire safety challenges: long evacuation times, high occupant density, and complex mechanical systems. Fire rated boards are commonly applied to:
-
Interior walls and partitions: Maintain compartmentation to slow fire spread
-
Ceilings and soffits: Protect structural elements and mechanical systems
-
Stairwells and elevator shafts: Ensure safe evacuation routes
7.2 Healthcare Facilities and Schools
Hospitals, clinics, and educational buildings host large numbers of people daily, making fire protection paramount. Applications include:
-
Patient rooms, classrooms, and laboratories: Protect occupants while supporting equipment and furnishings
-
Corridors and staircases: Maintain egress paths with reliable fire resistance
-
Operating theaters and specialized labs: Require boards that also resist moisture and facilitate hygiene
7.3 Public Transportation Hubs
Airports, metro stations, and bus terminals are high-traffic spaces where fire emergencies can escalate quickly. Fire rated boards are applied to:
-
Tunnel linings and platform walls: Contain flames and limit heat transfer
-
Ceiling panels and partitions: Ensure compartmentalization for crowd safety
-
Fire-rated doors and enclosures: Protect critical mechanical and electrical systems
7.4 Industrial Facilities and Warehouses
Factories, chemical plants, and storage warehouses often contain flammable materials or machinery that can ignite fires. Fire rated boards in these facilities serve to:
-
Partition hazardous zones: Contain fire and prevent cross-contamination
-
Ceiling linings and false ceilings: Protect structural components
-
Enclosures for machinery and electrical installations: Reduce fire propagation
7.5 Residential Applications
Even residential buildings benefit from fire rated boards, enhancing safety without sacrificing aesthetics. Typical uses include:
-
Shared walls in apartments and condominiums: Limit fire spread between units
-
Kitchen walls and ceilings: Protect areas prone to accidental ignition
-
Home theaters and utility rooms: Combine acoustic performance with fire resistance
By selecting fire rated boards appropriate for each zone, homeowners can reduce risk and improve long-term building performance.
8. How to Choose the Right Fire Rated Board
Selecting the appropriate fire rated board is critical for safety, compliance, and long-term project success. While many boards appear similar, their performance characteristics, certifications, and installation requirements differ. Here are the key considerations for choosing the right board:
8.1 Determine Required Fire Rating
Begin by reviewing local building codes and fire safety regulations. Consider:
-
Low-risk residential partitions: 30–60 minutes may suffice
-
High-risk zones (hospitals, laboratories, industrial areas): 90–120 minutes recommended
-
High-rise buildings and critical infrastructures: Ratings must meet code-mandated durations
Selecting the correct fire rating ensures adequate protection without over-specifying, which can unnecessarily increase costs.
8.2 Verify Certification and Test Reports
Only boards with authentic certifications should be used. Look for:
-
Recognized standards: EN 13501, ASTM E119, BS 476, ISO 834
-
Detailed fire test reports specifying duration, integrity, insulation, and smoke performance
-
Batch numbers and manufacturing dates for traceability
Authentic documentation gives confidence for architects, contractors, and regulatory authorities.
8.3 Consider Material Type and Performance
Different fire rated boards offer distinct advantages:
-
MgO boards: Moisture-resistant, eco-friendly, high durability, and non-combustible
-
Calcium silicate boards: High temperature resistance, structural strength
-
Fiber cement boards: Durable, versatile, suitable for interior and exterior use
Evaluate the fire rating in combination with environmental and structural requirements to ensure optimal selection.
8.4 Evaluate Installation Requirements
Installation affects both performance and cost. Consider:
-
Ease of cutting, shaping, and fastening
-
Compatibility with adhesives, coatings, or surface finishes
-
Labor skill level and availability of specialized tools
Proper installation ensures certified fire performance is maintained.
8.5 Assess Supplier Reliability
Reliable suppliers provide:
-
Certified, high-quality boards
-
Technical guidance and installation support
-
Post-purchase service for maintenance and replacement
Partnering with reputable suppliers reduces project risk and ensures compliance.
9. Conclusion
Fire rated boards are a critical component of modern construction, providing certified protection against fire while offering additional benefits such as moisture resistance, durability, sound insulation, and environmental sustainability. Understanding the differences between fire rated, fire resistant, and fireproof boards is essential for architects, engineers, and contractors to ensure building safety and regulatory compliance.
From high-rise buildings and hospitals to industrial facilities and residential projects, selecting the right board—whether gypsum, calcium silicate, fiber cement, mineral wool, or magnesium oxide (MgO) board—can make the difference between minimal fire protection and comprehensive, code-compliant safety. Proper installation, verification of certifications, and matching board type to application are key to maximizing performance and longevity.
Explore the best heat proof and heat resistant materials for safer construction. Learn their benefits, applications, and safety advantages.
Compare recessed vs non-recessed MgO boards. Learn features, applications, and tips to choose the right fire- and moisture-resistant board.
Compare MgSO4 board vs MgCl2 board: discover key differences, performance, and durability to choose the best mgo board for your project.




